- E-mail:BD@ebraincase.com
- Tel:+8618971215294
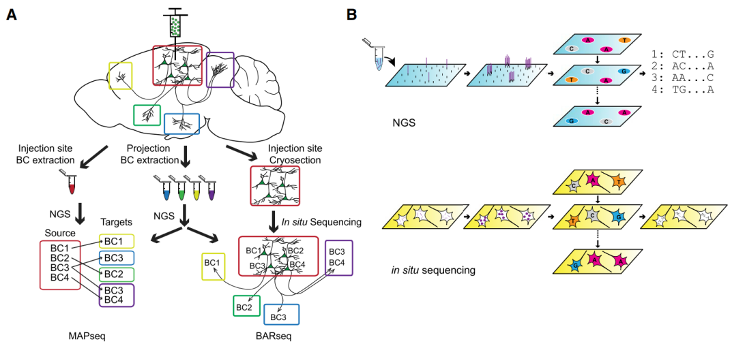
Features: Barcoding is a technique used in high-throughput sequencing to distinguish between multiple samples by attaching specific "tags" to each sample's sequence. These tags allow for the separation of data from different samples during subsequent data analysis. In other words, a barcode is a short sequence used to differentiate samples within the same "lane" of sequencing. Each sample is assigned a unique barcode, serving as an "identification card" for mixed samples in sequencing experiments.
The rabies virus vaccine strain SAD B19, expressing red fluorescent protein, for retrograde labeling. The Rab△G-mCherry-Barcode plasmid library was packaged with envelope protein ENVA, which only infects cells expressing the EnvA receptor and TVA, allowing for genetic targeting of interested cells in vivo. Fluorescently labeled barcode cells were isolated by flow cytometry, and the transcribed mRNA barcodes in the labeled cells were analyzed using scRNA-seq.
Gene/Insert name:Barcode
Tag/Fusion protein:mCherry
Titer:≥1.0e+08 IFU/mL
Volume:20 μL
Usually Ships in7 Business Days
Please provide us some information about the service you'd like to order.
( Select the service you'd like to purchase. )