- E-mail:support@braincase.cn
- Tel:18971216876
The retrograde transmonosynaptic system modified based on the SAD-B19 strain of rabies virus can mark the input network of specific types of neurons [1]. It has been used to solve a large number of neuroscience problems and has been widely promoted and applied in the field of neuroscience. . However, this system can only label a small number of upstream nerve cells across postsynapses, may ignore relevant input network connections, and is highly toxic. It is not conducive to long-term carrying of functional genes for neural activity detection or functional manipulation. Therefore, how to improve Its trans-synaptic efficiency and reduced toxicity are the directions of efforts of the neuroscience community. Codon-optimized chimeric glycoprotein (oG) can assist SAD-B19-ΔG to increase the trans-synaptic tracing efficiency by 20 times [2]. Many laboratories use oG-expressing adeno-associated viruses as auxiliary vectors to track nerves. Network upstream input [3-5], but it is highly toxic and can only be used for the analysis of structural networks.
The self-inactivated rabies virus modified on the basis of SAD-B19-ΔG can rapidly degrade the N protein related to viral replication. Adeno-associated viruses that can carry Cre or Flpo recombinase combined with expression functional probes are used for the preliminary development of functional networks. research, but it also has shortcomings such as complex preparation process, weak self-expression, and inability to carry functional probes [6], and it is unknown whether it can be used for efficient cross-synaptic labeling and manipulation of functional networks.
Chatterjee et al. reported the nontoxic SAD-B19-ΔGL with double deletion of G and L proteins, but it has only very weak expression ability and can only be expressed through AAV viruses or transgenic animals carrying Cre or Flpo recombinase combined with expression functional probes. It is used for activity monitoring and manipulation of functional networks. At the same time, because the L gene is relatively large, it is necessary to adopt a suitable helper virus vector strategy or to create transgenic animals expressing L to achieve cross-single synapse [7]. Reardon et al. [8] established a retrograde trans-monosynaptic system modified by CVS-N2c strain rabies virus. After the genome deleted its own glycoprotein N2cG, through reverse compensation of N2cG, its retrograde trans-synaptic system was compared with the SAD-B19 vaccine strain. The touch ability is significantly enhanced and the toxicity to neurons is further reduced. Functional probes such as calcium ion probes and optogenetic probes can be expressed for the analysis of functional circuits. Therefore, they have more advantages in neural circuit tracing, but they are also It has shortcomings such as very difficult preparation and low titer, so it is rarely reported in subsequent loop tracing studies.
Judging from the above-mentioned current situation, the development of attenuated and efficient reverse cross-single synapse tool viruses that take into account both structural and functional network analysis is still an urgent need in the entire field of neuroscience.
Recently, Xu Fuqiang’s team at the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, published a study in the 2023 issue 8 of the journal "Chinese Neuroregeneration Research (English Edition)" and found that B19G-related cell lines can be used to quickly package and prepare high-titer CVS-N2c- ΔG, and by infecting novel N2cG and EnvARVG cell lines with high-titer B19G-pseudotyped CVS-N2c-ΔG, high-titer N2cG-encapsulated CVS-N2c-ΔG and EnvARVG-pseudotyped CVS-N2c-ΔG can be quickly obtained. .
Through in vivo studies, it was found that: ① The efficiency of retrograde transduction of projection neurons by N2cG-wrapped CVS-N2c-ΔG is significantly better than that of AAV-Retro; ② The retrograde transduction efficiency of CVS-N2c-ΔG across single synapses is better than that of commonly used SAD-B19-ΔG; ③ CVS-N2c-ΔG can be equipped with functional probes for neural activity monitoring, and the time window can be maintained for up to 3 weeks; ④ CVS-N2c-ΔG can express sufficient recombinase for effective transgenic recombination. The development of attenuated, highly efficient retrograde viral tracers across single synapses may provide a useful tool for structural and functional studies of neural circuits.
Retrograde labeling of viruses can be used to dissect upstream neural networks that project to specific brain regions. Previous research by Xu Fuqiang's team reported that N2cG-wrapped SAD-B19-ΔG has the ability to efficiently retrogradely label upstream networks in specific brain regions along axon terminals [9]. If the N2cG-wrapped CVS-N2c-ΔG virus can also be efficiently retrogradely labeled, it will be more conducive to structural loop labeling and functional manipulation. Currently, commonly used retrograde labeling tools mainly use adeno-associated virus (AAV), such as AAV2-Retro and AAV9-Retro, which are equally efficient, but they have brain region selectivity [9-11]. Therefore, Xu Fuqiang and others also compared the reverse labeling capabilities of CVS-N2c-ΔG (N2cG) and AAV9-Retro. CVS-N2c-ΔG (N2cG) and AAV9-Retro were mixed and injected into the caudate putamen (dorsal striatum) brain area. After 14 days, it was found that CVS-N2c-ΔG (N2cG) had better retrograde labeling efficiency than AAV9-Retro. , can efficiently label neural pathways with low labeling efficiency by AAV9-Retro, such as VTA/SNc→dorsal striatum pathway (Figure 1).
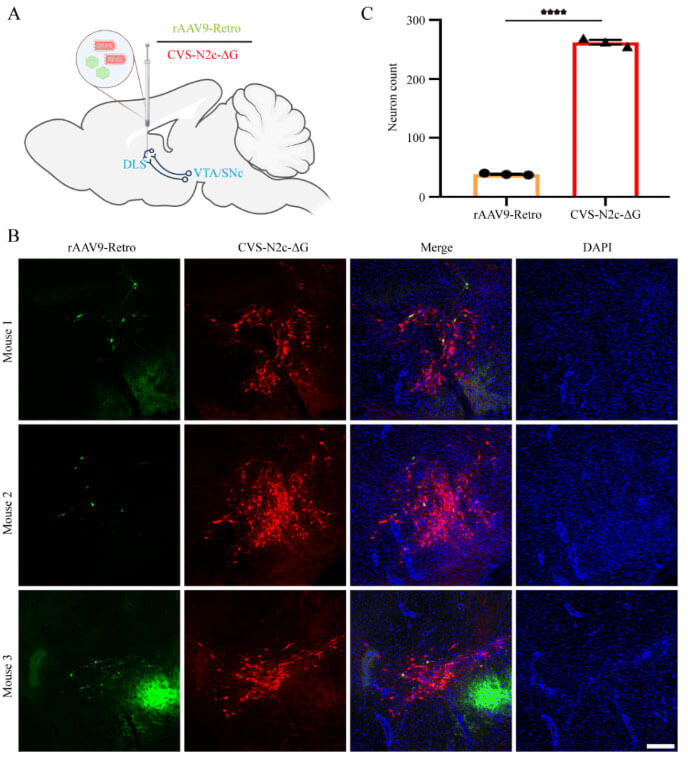
Figure 1: CVS-N2c-ΔG (N2cG) retrogradely labels projection neurons more efficiently than AAV9-Retro (Source: Lin et al., Neural Regen Res, 2023)
Virus strains from different sources may have different transsynaptic efficiencies or other tropisms when binding to outer membrane glycoproteins from different sources. In order to verify whether the codon-optimized chimeric glycoprotein can assist CVS-N2c-ΔG in efficient retrograde trans-monosynaptic spread, AAV carrying the codon-optimized chimeric glycoprotein and TVA carrying controlled expression of Cre recombinase were used as Helper viruses were mixed and injected into the ventral hippocampus of Thy1-Cre transgenic mice. Three weeks later, EnvARVG-wrapped CVS-N2c-ΔG and SAD-B19-ΔG were injected at the same site. CVS-N2c-ΔG was visible on day 7. The transsynaptic efficiency of the /oG system is higher than that of the SAD-B19-ΔG/oG system, which is 3-4 times that of the latter (Figure 2). Therefore, CVS-N2c-ΔG/oG can serve as an important retrograde transmonosynaptic system and is expected to be used to analyze the upstream input connection network of specific types of neurons in specific brain regions.
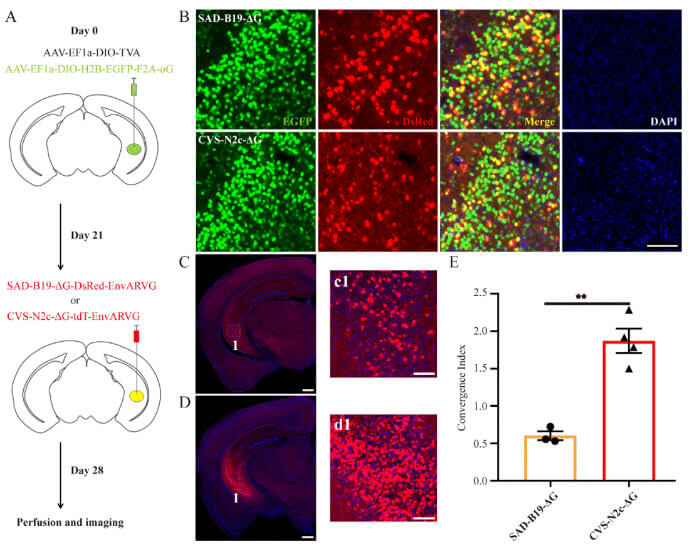
Figure 2: The retrograde trans-monosynaptic efficiency of the CVS-N2c-ΔG/oG system is better than that of the SAD-B19-ΔG/oG system (Source: Lin et al., Neural Regen Res, 2023)
In short, Xu Fuqiang's team successfully established an improved production system that can be used to quickly rescue and prepare high-titer CVS-N2c-ΔG viruses, and the CVS-N2c-ΔG viruses prepared by the new method are retrograde in neural circuits. Excellent performance in labeling, cross-single synapse targeting, functional monitoring and transgenic recombination, which will facilitate structural and functional studies of neural circuits and elucidation of disease mechanisms. However, the toxicity of the CVS-N2c-ΔG virus has not been completely eliminated. Next, it needs to be further modified to weaken the toxicity and make it suitable for carrying functional genes for longer-term functional control and monitoring.
Xu Fuqiang is a researcher at the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, a National Distinguished Young Scholar, and a distinguished professor at the University of Science and Technology of China. In recent years, it has mainly developed technical methods and tools for analyzing the structure and function of neural circuits and cell gene therapy. The 600 transformation products invented have been used by more than 1,000 laboratories at home and abroad. Participants of the 5 viral vector technology training courses held There are more than 3,000 people, and most of the results are "shareholding" with technology. He has published 140 papers in journals including Science, Nature, Nature Biotechnology, Nature Neuroscience, Neuron, Nature Communications, Science Advances, and PNAS, and applied for more than 60 patents.
Original link:
https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.358618
Xu Fuqiang Laboratory